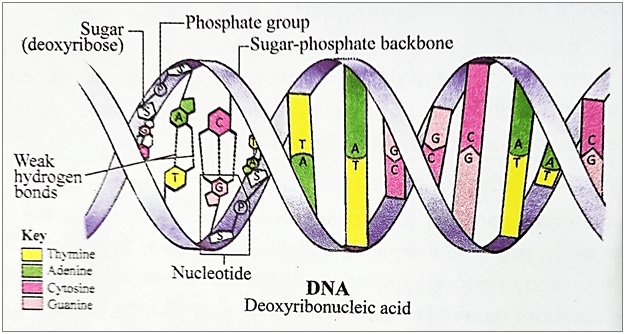
DNA:
It stands for Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid. DNA has nitrogen bases in the form of adenine, guanine, cytosine, and Thymine. It has the blueprint for all the hereditary characteristics of an organism. DNA has a double helical structure with two antiparallel strands held by H-bonds.
RNA:
It stands for Ribo Nucleic Acid. RNA has uracil instead of thymine, and adenine and cytosine are also present. They are single-stranded and play an important role in protein synthesis. There are mainly three types of RNA:
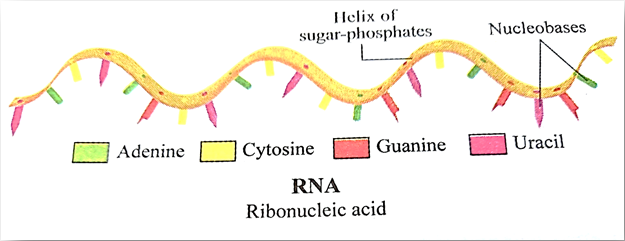
- r-RNA
- m-RNA
- t-RNA
Difference between DNA and RNA:
| Parameter | DNA | RNA |
| Full Form | Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid | Ribo Nucleic Acid |
| Stranded | Double Stranded | Single Stranded |
| Pentose Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Bases | The bases in DNA are Adenine (‘A’), Thymine (‘T’), Guanine (‘G’) and Cytosine (‘C’). | The bases in RNA are Adenine (‘A’), Uracil (‘U’), Guanine (‘G’) and Cytosine (‘C’). |
| Base Pairing | Adenine and Thymine pair (A-T) Cytosine and Guanine pair (C-G) | Adenine and Uracil pair (A-U) Cytosine and Guanine pair (C-G) |
| Structure | DNA has two nucleotide strands which consits of its phosphate group, five carbon sugar and four nitrogen containing nucleobases such as Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine. | RNA composed of its phosphate group, five carbon sugar and four nitrogen containing nucleobases such as Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine and Guanine. |
| Propagation | DNA is self-replicating | RNA is synthesized from DNA when needed. |
| Location | DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell and in mitchondria. | RNA is found in a cells nucleus, its cytoplasm and its ribosome. |
| Function | The blueprint of biological guideline that a living organism must follow to exist and remain functional. Medium of long-term, stable storage and transmission of genetic information. | RNA helps to carry out DNA's blueprint guidelines. Transfers genetic code needed for the creation of proteins from the nucleus to the ribosome. |